dry and liquid cycles in the autoclave|autoclave liquid vs gravity : specialty store The sterilization cycle in an autoclave with drying consists of several steps: Purge . Autoclaves use high-pressure steam for a designated amount of time to kill pathogens on objects of various shapes and sizes. Common examples are surgical tools, lab instruments, and .
{plog:ftitle_list}
For use with 8 Combitips™ Advanced (0.1 to 10 mL) Supplier: Eppendorf™ 0030089758
what temp is an autoclave
This article delves into the most prevalent sterilization cycles employed in autoclaves, providing a simplified exposition to facilitate informed decision-making in selecting the optimal cycle for your specific sterilization requirements.
The sterilization cycle in an autoclave with drying consists of several steps: Purge . Flash Cycle (Immediate-Use Cycle): This is a rapid cycle used when items need to be sterilized quickly, often in emergency situations. The flash cycle has a higher temperature .To be effective, the autoclave must reach and maintain a temperature of 121° C for at least 30 minutes by using saturated steam under at least 15 psi of pressure. Increased cycle time may be necessary depending upon the make-up and volume of the load. The rate of exhaust will depend upon the nature of the load. Dry material can be treated in a fast
describe autoclaving process
sterilization time temperature chart
Autoclave sterilisation is one of the most effective methods of sterilisation out there. By generating high-pressure steam, pesky microorganisms such as spores can be quickly denatured and killed. Typically, the gravity cycle, vacuum cycle, and liquid cycle are the three most common cycles you will encounter when it comes to autoclave sterilisation.
Liquids cycles may use a load probe to measure and control the Sterilization phase of the cycle from within the actual liquid load. Vacuum. This cycle type is similar to a Gravity cycle, except for what happens before the Sterilization phase. Multiple pulses of vacuum followed by steam injection are used to remove air from the chamber and the load.Autoclave Cycle Types • Fast exhaust or gravity cycle – use for bagged tools (scalpels and scissors) • Slow exhaust or liquid cycle – use for liquids and slow steam evacuation • Dry cycle– use for dry goods such as glassware or plastics, e.g., pipet tips. This cycle is In general, there are three main types of steam sterilization cycles: gravity, vacuum, and liquid. All three use high temperature and high pressure for disinfection; however, each cycle uses a slightly different custom process to maximize disinfection conditions for certain items. Gravity cycle. Gravity is the simplest and most common autoclave .Incorrect selection of cycle may damage the autoclave, cause liquid to boil over or bottles to break. Start your cycle and fill out the autoclave user log. A completed cycle usually takes between 1 to 1.5 hours. Check chamber/jacket pressure gauge for minimum pressure of 20 pounds per square inch (psi). Close and lock door.
Dry hard items (unwrapped or in porous wrap); and/or; . plastic materials that will withstand fast-exhaust cycles can melt using the Liquid cycle due to prolonged exposure to heat. . It can serve as an easy visual means of identifying items that have been through an autoclave cycle from those that have not. However, this tape it is NOT a .
%PDF-1.7 %âãÏÓ 4276 0 obj > endobj 4288 0 obj >/Encrypt 4277 0 R/Filter/FlateDecode/ID[1564B57341670E45ABF57AA58477559A>]/Index[4276 29]/Info 4275 0 R/Length 79 . Gravity is the simplest and most common of the autoclave cycles. Like the name suggests, the cycle relies on gravity to replace air with steam. When steam is pumped into the chamber, it rises to the top because it has a lower density than air. . Contrary to the first two types of sterilization, the liquid cycle does not involve sterilizing .Autoclaves are also used for industrial applications such as curing composite resins and material testing, in the aeronautical industry. We'll focus on the autoclave sterilization cycle process and walk you through the different autoclave cycle stages. After reading all the material in this series you’ll know how an autoclave works.
A drying time of at least 10 minutes is usually recommended. If the sterilizer does not have a drying cycle, the manufacturer’s instructions on how to dry the load should be consulted. Processed items should be visibly dry when they are removed from the sterilizer. Today, there are tabletop sterilizers that permit drying with the door closed. The two basic types of steam sterilizers (autoclaves) are the gravity displacement autoclave and the high-speed prevacuum sterilizer. In the former, steam is admitted at the top or the sides of the sterilizing chamber and, because the steam is lighter than air, forces air out the bottom of the chamber through the drain vent.The sterilization cycle in an autoclave with drying consists of several steps: Purge phase. . The accompanying image illustrates the operation of an AHS-DRY Series autoclave during the drying phase. These models are equipped with electric heating elements and an integrated water tank. . Dive into the liquids cycle and learn how to ensure a .
describe the use of an autoclave in microbiology laboratory
Never, ever autoclave a sealed container; it becomes a bomb. There are two safe, effective ways to address boil over. They’re cheap and easy: Use bigger bottles; Chose the right autoclave cycle; Running Research Lab Autoclave Liquid Cycles in the Real World “Dry cycles” tend to either pull a vacuum on the chamber, or permit one to .
Discover how the gravity cycle in autoclaves facilitates efficient and cost-effective sterilization. . particularly bulky liquid loads, even after the cycle has concluded and the door is opened. . and storing them in a clean, dry environment. In the .
5 LIQUID CYCLE • Type I borosilicate glass containers with . (in autoclave bags; can be wet & dry tubes, plates, etc.) PRE-VACUUM . STERILIZE TEMP121º C . STERILIZE . TIME = 30 to 45 min. COOL TIME = 2 to 5 min. RUN TIME 40 to 55 min. NOT RECOMMENDED FOR LIQUIDS OR MEDIA, LIGHTER WEIGHT PLASTIC CONTAINERS OR DRY ITEMS WHICH WILL
The liquids cycle in an autoclave operates on a modified gravity cycle, tailored to control the cooling phase and extend the duration of the heating phase. Although the sterilization temperature employed is 121°C, the duration depends significantly on the volume of the liquids and the size of the containers. . This ensures that if a liquid .Add 1/4 to 1/2 inch of water to the tray so the bottles will heat evenly during liquid cycles. . Wear heat-resistant gloves when opening the autoclave door after a cycle. If there is a sharps hazard (e.g. biological waste), wear heat AND cut resistant gloves. . Before removing autoclaved items, wait 5 minutes for loads containing only dry . Liquid cycles are designed to gradually increase and decrease temperature to avoid rapid boiling, and containers should only be partially filled to allow for expansion. Q: What is the significance of drying in the autoclave cycle? A: The drying phase is crucial for removing moisture from sterilized items, preventing microbial recontamination . This includes standard PPE-safety glasses, lab coats, and closed-toe shoes and heat-resistant gloves. Use an apron and face shield when handling liquid samples. At the autoclave, first open the door and check for any hazards within. Load liquid and dry materials separately, as they require different autoclave cycles.
Dry heat sterilizers are available in both batch and continuous configurations. Continuous configurations typically have a tunnel. . For many liquid cycles air removal is not performed; however, it is important to ensure that a system is used to ensure uniform heat distribution within the chamber (PDA 2007). The containers in a load heat do .Dry items (e.g. tips, tubes, empty glass flasks) = Cycle 4; Autoclave trash = Cycle 6; Autoclave liquid trash = Cycle 3. As a general rule of them, dry biohazardous trash should be autoclaved for a minimum of 2 hours at 121 degrees celsius, and liquid biohazardous trash should be autoclaved for a minimum of 1 hour. Press “Start” to start cycle.
Sterilization Cycle Verification. A sterilization process should be verified before it is put into use in healthcare settings. All steam, ETO, and other low-temperature sterilizers are tested with biological and chemical indicators upon installation, when the sterilizer is relocated, redesigned, after major repair and after a sterilization failure has occurred to ensure they are . As we’ve discussed before, the best autoclave procedure for running liquid loads is trickier than just loading up the autoclave and choosing the “liquid cycle.”Follow these four rules and you’ll largely avoid trashing your autoclave chamber, plumbing, and drain while losing your liquids to evaporation, boil over, or burst bottles: Most lab autoclaves have preset cycles for dry goods (gravity; fast exhaust) and liquids (liquid; slow exhaust). If sterilizing liquids, it is imperative that the liquid cycle is selected to prevent boil over during the exhaust portion of the cycle. Again, liquids should be allowed to cool sufficiently before removal as disturbing the liquids .
To address this issue, gravity autoclaves can be equipped with a post-cycle vacuum feature to dry the load. If an autoclave is equipped with this feature, it will run a normal gravity cycle and, once the load is sterilized, a vacuum will pull the steam and . Pre-vacuum Autoclave Cycle. Pre-vacuum cycles start by evacuating the air from the chamber before introducing steam. This method is more effective at sterilising complex items and porous loads. Ideal applications include: Wrapped surgical instruments. Porous materials. Surgical gowns and drapes. Liquid Cycle
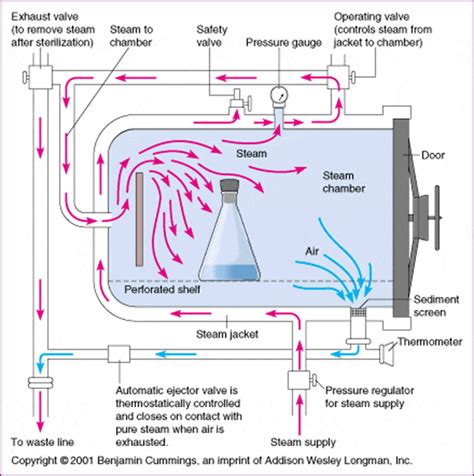
liquid sterilization autoclave procedure
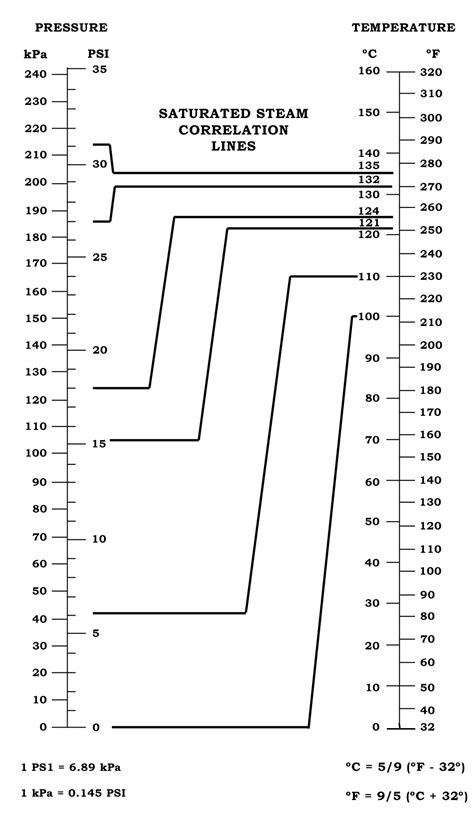
In other words, it is a test whose results diagnose the correct functioning of the autoclave. The Bowie & Dick test indicates whether steam penetration into the test pack was .
dry and liquid cycles in the autoclave|autoclave liquid vs gravity